Introduction
Cardiac surgery has come a long way from traditional open-heart procedures to highly sophisticated, minimally invasive, and robotic-assisted techniques. These innovations have not only made surgeries safer but have also improved recovery times, reduced complications, and enhanced long-term outcomes for patients with heart disease.
This article explores how modern advancements in cardiac surgery — from coronary artery bypass grafting to robotic precision — are transforming heart care around the world.
The Evolution of Cardiac Surgery
1. The Early Era: Open-Heart Surgery
The history of cardiac surgery dates back to the early 20th century when open-heart procedures were performed using a heart-lung machine to keep blood circulating while the heart was stopped. Although lifesaving, these surgeries involved large incisions, significant blood loss, and lengthy hospital stays.
Open-heart surgery revolutionized heart care but also came with challenges — postoperative pain, long recovery periods, and higher risks of infection.
2. The Introduction of Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG)
One of the most important breakthroughs in cardiac surgery was coronary artery bypass grafting (CABG), developed in the 1960s. This procedure restores normal blood flow to the heart by bypassing blocked arteries using healthy vessels taken from other parts of the body, such as the leg or chest.
Benefits of CABG include:
- Improved blood flow to the heart muscle
- Reduced chest pain (angina)
- Decreased risk of heart attack
- Improved overall heart function
While traditional CABG remains a gold standard, it has evolved into minimally invasive and off-pump techniques, making the procedure safer and less traumatic.
Modern Innovations in Cardiac Surgery
1. Minimally Invasive Cardiac Surgery (MICS)
Unlike open-heart surgery, minimally invasive cardiac surgery uses small incisions between the ribs, avoiding the need to open the breastbone (sternum).
Common MICS procedures include:
- Mitral valve repair or replacement
- Aortic valve replacement
- Coronary artery bypass
- Atrial septal defect (ASD) closure
Advantages:
- Smaller incisions and less scarring
- Reduced risk of infection
- Shorter hospital stays
- Faster recovery time
This approach has become increasingly popular for patients seeking less invasive options with excellent outcomes.
2. Off-Pump (Beating Heart) Surgery
Traditional CABG requires stopping the heart and using a heart-lung machine. In contrast, off-pump bypass surgery is performed while the heart is still beating, reducing the complications associated with cardiopulmonary bypass.
Key benefits:
- Reduced risk of stroke
- Less inflammation and blood loss
- Quicker postoperative recovery
This technique is particularly beneficial for elderly patients or those with multiple health conditions.
3. Transcatheter Procedures (TAVR & TMVR)
Another groundbreaking development is the rise of transcatheter procedures, which allow surgeons to repair or replace heart valves without open surgery.
- TAVR (Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement): Replaces a damaged aortic valve using a catheter inserted through the leg artery.
- TMVR (Transcatheter Mitral Valve Repair): Corrects a leaking mitral valve without open-heart surgery.
Benefits:
- Ideal for high-risk or elderly patients
- No need for general anesthesia in some cases
- Shorter hospital stays and recovery times
These catheter-based techniques are changing the landscape of heart valve treatment.
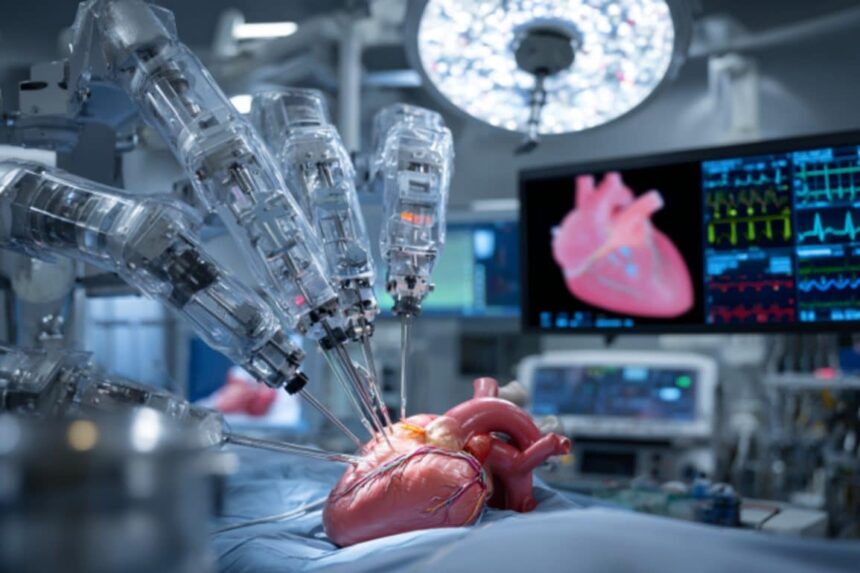
4. Robotic-Assisted Cardiac Surgery
One of the most exciting advancements in heart surgery is robotic-assisted technology. Using a robotic system controlled by a surgeon, precise instruments perform complex heart procedures through tiny incisions.
How it works:
The surgeon sits at a console and manipulates robotic arms equipped with miniaturized surgical tools and a high-definition 3D camera. The system enhances precision, dexterity, and visibility beyond human capabilities.
Common robotic-assisted surgeries:
- Mitral valve repair
- Coronary artery bypass (robotic CABG)
- Atrial fibrillation (AFib) ablation
Benefits of robotic cardiac surgery:
- Greater precision and accuracy
- Minimal scarring and blood loss
- Reduced postoperative pain
- Faster recovery and return to normal activities
Robotic-assisted surgery is the future of cardiac care — blending human expertise with robotic precision for unmatched outcomes.
5. Hybrid Cardiac Procedures
In some cases, surgeons combine traditional surgical techniques with catheter-based interventions to achieve optimal results. These are known as hybrid procedures.
Example: A patient may undergo a minimally invasive bypass on one artery and stent placement on another in the same session.
This approach minimizes trauma while providing comprehensive treatment for complex heart diseases.
The Role of Technology and Artificial Intelligence
Emerging technologies such as artificial intelligence (AI), 3D imaging, and virtual reality (VR) are enhancing surgical planning and precision.
- AI algorithms help identify optimal surgical strategies.
- 3D printing allows surgeons to create patient-specific heart models before surgery.
- VR systems enable simulation training for complex cardiac procedures.
These tools are revolutionizing pre-surgical assessment, reducing risks, and improving patient safety.
Post-Surgery Recovery and Future Outlook
Recovery from modern cardiac surgeries is now faster than ever. Most patients can return home within a week of surgery and resume normal activities within a few weeks.
With continuous advancements in robotics, imaging, and telemedicine, the future of cardiac surgery promises even less invasive procedures and more personalized treatment approaches.
Conclusion
From traditional bypass operations to cutting-edge robotic and transcatheter techniques, cardiac surgery has entered a new era of precision, safety, and efficiency. These innovations are saving more lives than ever before, offering patients faster recovery, fewer complications, and better quality of life.
As technology continues to evolve, the future of heart surgery will likely become even more patient-centered, minimally invasive, and digitally advanced.
FAQs
1. What is the most common type of heart surgery today?
Coronary Artery Bypass Grafting (CABG) remains one of the most common and effective heart surgeries worldwide.
2. How long does it take to recover from minimally invasive heart surgery?
Most patients recover within 2–4 weeks, compared to 6–8 weeks for traditional open-heart procedures.
3. Is robotic heart surgery safe?
Yes. Robotic-assisted heart surgery is highly precise and safe when performed by experienced surgeons. It typically results in smaller incisions and faster recovery.
4. What is TAVR, and who is it for?
TAVR (Transcatheter Aortic Valve Replacement) is a minimally invasive alternative to open-heart valve replacement, often recommended for elderly or high-risk patients.
5. What is the future of cardiac surgery?
The future lies in AI-assisted robotic systems, 3D imaging, and hybrid procedures, which promise greater precision and faster, safer recoveries.