Introduction
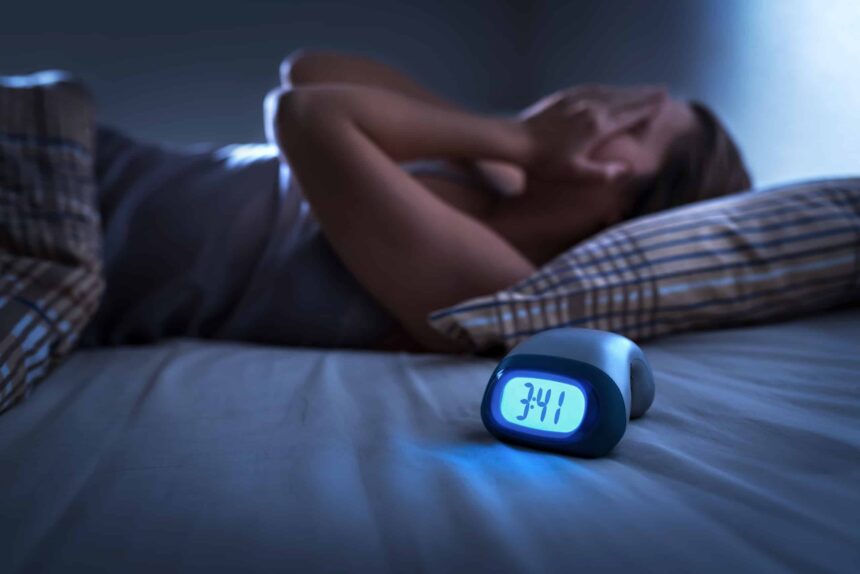
Sleep is one of the most vital yet often overlooked pillars of good health. While we all know that sleep helps the body rest and recharge, its effect on mental and emotional health is even more profound. Quality sleep not only sharpens focus and memory but also stabilizes mood, reduces stress, and enhances emotional resilience. In this article, we’ll explore how sleep impacts your mood, focus, and emotional stability — and how improving your sleep habits can lead to a healthier, happier life.
The Science Behind Sleep and Mental Health
When you sleep, your brain doesn’t simply “shut down.” Instead, it goes through multiple stages of restoration, repairing cells, consolidating memories, and balancing hormones that influence mood and alertness.
A lack of quality sleep disrupts these processes, leading to irritability, poor concentration, and emotional instability.
Key sleep stages that affect your mind and mood include:
- REM (Rapid Eye Movement) Sleep: This is when dreaming occurs and emotional regulation happens.
- Deep Sleep (Slow-Wave Sleep): This stage restores the body and helps consolidate memories.
- Light Sleep: Plays a role in maintaining cognitive performance and alertness.
When these stages are interrupted, your mental clarity and emotional balance suffer.
How Sleep Affects Mood Regulation
Poor sleep has an immediate impact on how you feel. Even one night of inadequate rest can lead to irritability, frustration, or sadness. Over time, sleep deprivation increases the risk of developing mood disorders such as depression and anxiety.
Here’s how it works:
- Reduced serotonin and dopamine: These neurotransmitters regulate happiness and motivation.
- Overactive amygdala: The amygdala — the brain’s emotional control center — becomes more reactive, making you more sensitive to stress and negativity.
- Increased cortisol: The stress hormone cortisol rises with poor sleep, making you feel more anxious and tense.
In short, sleep helps balance your emotional responses, while lack of sleep magnifies negative emotions and weakens your ability to cope with daily challenges.
Sleep and Focus: Why Rest Is Key for Cognitive Performance
Sleep plays a crucial role in how well your brain processes, stores, and retrieves information.
When you don’t get enough rest:
- Attention span decreases.
- Decision-making becomes slower.
- Memory retention weakens.
A well-rested brain, on the other hand, improves creativity, problem-solving, and focus — essential for work, learning, and personal growth.
Interesting Fact:
Research from the National Institutes of Health (NIH) shows that sleep-deprived individuals experience a 40% reduction in their ability to learn new things because the brain’s hippocampus (responsible for memory formation) becomes less active.
Sleep and Emotional Stability
Your emotional stability depends largely on how well your brain processes and regulates emotions during sleep. When you get adequate rest, your mind resets and prepares for emotional challenges.
Without it, even minor inconveniences can feel overwhelming.
Effects of Sleep Deprivation on Emotional Stability:
| Sleep Issue | Emotional Impact |
|---|---|
| Insomnia | Heightened irritability and sadness |
| Inconsistent Sleep Schedule | Mood swings and impulsive behavior |
| Sleep Apnea | Fatigue and reduced emotional control |
| Short Sleep Duration (<6 hrs) | Increased stress and anxiety |
This is why consistent, high-quality sleep is one of the most effective ways to build emotional resilience and mental strength.
How Sleep Impacts Mental Health Disorders
Chronic sleep deprivation doesn’t just affect daily mood — it’s also linked to long-term mental health issues, including:
- Depression: Insufficient sleep reduces serotonin, contributing to depressive symptoms.
- Anxiety Disorders: Lack of rest heightens the body’s fight-or-flight response.
- Bipolar Disorder: Poor sleep can trigger manic or depressive episodes.
- ADHD: Irregular sleep disrupts focus and self-regulation in both adults and children.
Improving sleep hygiene can significantly reduce the severity of these conditions and improve overall mental health.
Tips to Improve Sleep Quality and Mental Wellness
1. Stick to a Consistent Sleep Schedule
Go to bed and wake up at the same time every day — even on weekends. This helps regulate your body’s internal clock.
2. Limit Screen Time Before Bed
The blue light emitted by phones and computers disrupts melatonin production, making it harder to fall asleep.
3. Create a Relaxing Night Routine
Try meditation, deep breathing, or reading before bed to calm your mind and prepare your body for rest.
4. Watch What You Eat and Drink
Avoid caffeine, nicotine, and heavy meals close to bedtime. Opt for calming drinks like chamomile tea instead.
5. Make Your Bedroom Sleep-Friendly
Keep your room cool, dark, and quiet. A comfortable mattress and pillow can make a huge difference.
6. Exercise Regularly
Engaging in moderate exercise during the day helps improve sleep quality and reduce anxiety levels.
The Benefits of Quality Sleep on Daily Life
Getting enough quality sleep has numerous benefits beyond just improving mood:
- Better emotional control and patience
- Improved decision-making and problem-solving
- Higher energy and productivity levels
- Stronger immune system and physical health
- Enhanced relationships and social interactions
Simply put, a well-rested mind is more resilient, optimistic, and capable of handling life’s ups and downs.
Conclusion
Sleep is not a luxury — it’s a necessity for mental, emotional, and physical well-being. By prioritizing good sleep habits, you can stabilize your mood, enhance focus, and strengthen your emotional stability. Think of sleep as daily maintenance for your brain — a natural way to reset, recover, and rise stronger every day.