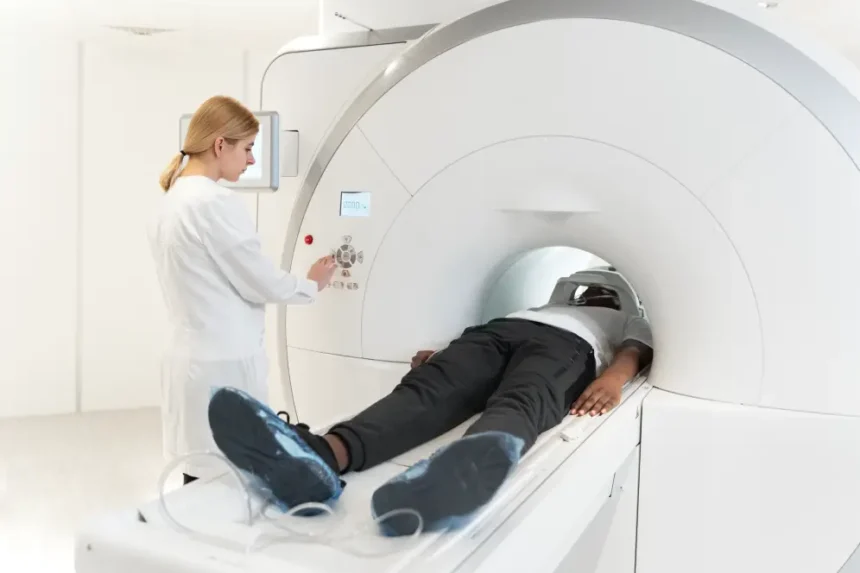
Metabolic disorders often involve complex changes within the body that are not always visible through standard diagnostic methods. Nuclear medicine plays a key role in detecting these conditions by evaluating how organs and tissues function at a cellular level. This functional imaging helps clinicians identify abnormal metabolic activity early, supporting accurate diagnosis.
What Are Metabolic Disorders?
A metabolic disorder happens when abnormal chemical reactions in the body disrupt the process of converting food to energy. Here are some warning signs that patients should watch for:
- Fatigue or weakness: Feeling tired all the time is a common sign that the body is not producing or using energy correctly.
- Unexplained weight changes: Sudden weight loss or gain without a change in diet may indicate a metabolic disorder.
- Abdominal pain: Conditions affecting organs such as the liver, gallbladder, or stomach often cause persistent pain in the abdomen.
- Nausea or vomiting: These symptoms often occur when the digestive system cannot process food properly.
- Skin changes: Yellowing of the skin or other texture changes can indicate that the liver or kidneys are not filtering toxins effectively.
If a patient notices these persistent signs, a doctor may recommend ordering nuclear medicine tests to investigate further.
How Does Nuclear Medicine Work?
Nuclear medicine is an advanced diagnostic modality that uses radioactive substances to evaluate conditions and diseases. This method allows doctors to observe how organs and tissues are functioning in real time. It is a useful tool for physicians who need to examine biological processes to identify the root cause of a symptom.
The process involves the use of a radiotracer, a tiny amount of radioactive material. Once the radiotracer is within the body, it travels to the target area and emits gamma rays. A special machine, often called a gamma camera, detects this energy and creates detailed images on a computer. These images show where the radiotracer has accumulated, indicating high chemical activity or metabolism in that area.
How Are Abnormalities Found?
Nuclear medicine exams are used to detect metabolic issues and organ dysfunction. Here are some of them:
- Gastric Emptying Study (GES): This test assesses the time required for the stomach to empty into the small intestine.
- Glomerular Filtration Rate (GFR): This test assesses how effectively the kidneys filter waste from the blood, a key indicator of kidney disease severity.
- Hepatobiliary Scan: This imaging test assesses the function of the bile ducts, gallbladder, and liver to detect inflammation or leaks that affect digestion.
- Thyroid Uptake Scan: This procedure assesses the thyroid gland in detail to diagnose conditions such as hyperthyroidism or nodules.
- Positron Emission Tomography (PET): PET scans assess organ and tissue function to detect abnormal activity.
These tests provide concrete data on how well the body performs its chemical processes.
How Do Results Guide Care?
Once the images are captured, a board-certified nuclear medicine specialist or radiologist interprets them to understand the results. They look for patterns in how the radiotracer was absorbed or processed by the body to identify dysfunction. This information is then sent to the patient’s doctor to inform the development of a comprehensive treatment plan. The results from radioactive tracer imaging can reveal functional changes before physical changes in the organ are visible. This allows for earlier treatment intervention, leading to better long-term outcomes for the patient.
Schedule Your Nuclear Medicine Appointment
Nuclear medicine offers a unique approach to the body’s chemical processes and functions. It is a method for detecting and managing metabolic disorders that conventional scans may otherwise miss. Doctors can visualize the body’s anatomy and how it functions internally using functional imaging. If you are experiencing symptoms of a metabolic disorder or need a specialized evaluation, contact a medical imaging center near you to schedule your nuclear medicine appointment today.