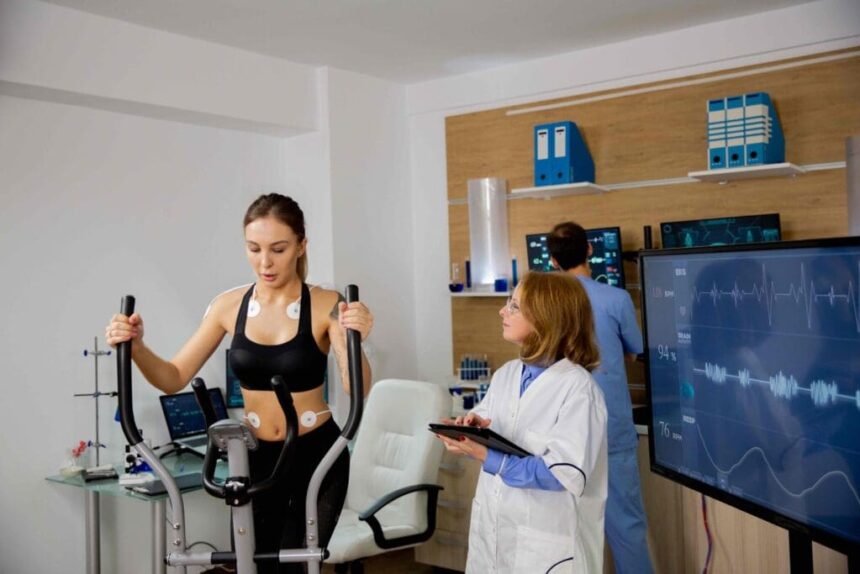
Sports medicine, which focuses on physical fitness and the treatment of sports and exercise injuries, is a vital branch of healthcare. While it helps athletes and active individuals return to peak performance safely and effectively, it also supports their ongoing health. This field includes both conservative management and complex surgery.
Non-Surgical Sports Medicine Treatments
Many sports injuries respond well to conservative treatments if patients follow their physician’s advice. Physicians often start with the least invasive methods to promote healing and restore function. Corrective biomechanics uses orthotics and braces to align the body during movement. These devices support injured joints, and they prevent further damage as you heal. Medications help manage pain and inflammation during recovery. NSAIDs reduce swelling, but use them only with a doctor’s guidance.
For more targeted relief, specialists sometimes administer corticosteroid injections directly into the affected area. Advanced injectable therapies have become increasingly common in modern sports medicine practices. Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) therapy utilizes a patient’s own blood components to support tissue repair. Viscosupplementation involves injecting a gel-like fluid into a joint, so the joint is lubricated and has improve movement.
Physical Therapy and Rehabilitation
Physical therapy is the cornerstone of sports-related recovery, and used for almost all sports injuries and conditions. It focuses on strengthening muscles, improving flexibility, and restoring the range of motion in affected joints. Therapists design specific exercise programs and tailor them to meet each patient’s unique needs. This personalized approach checks that the injured area heals correctly without being overstressed.
Orthobiologics are biological substances used to help musculoskeletal injuries heal more quickly. These treatments are often integrated into rehabilitation plans, as they harness the body’s natural healing abilities. When combined with physical therapy, orthobiologics sometimes delay or eliminate the need for surgery.
Advancements in technology and research have led to new orthobiologic treatments like PRP and stem cell therapy, which reduce inflammation, promote tissue regeneration, and accelerate recovery. PRP uses a concentrated sample of a patient’s blood platelets to stimulate healing in damaged tissues, and stem cell therapy focuses on using stem cells’ regenerative potential to repair cartilage, tendons, or ligaments. Together, these innovative approaches offer promising options for patients seeking non-invasive treatments for musculoskeletal conditions.
Surgical and Advanced Procedures
When conservative measures fail to provide relief, surgery becomes necessary to restore function. Modern advancements have made many procedures less invasive and more effective. Minimally invasive arthroscopic procedures use small incisions and cameras to repair joints with precision. Surgeons fix torn tissues through small openings, so patients often recover faster. Cartilage restoration procedures, such as OATS and MACI, address damaged joint surfaces. These techniques repair cartilage defects and help preserve the joint over time. Complex injuries may need more significant interventions for stability and longevity. Meniscus transplants replace a damaged meniscus with donor tissue, while complicated repairs stitch torn tissue back together.
Take The Next Step
Understanding the full spectrum of sports medicine options helps patients make informed decisions about their healthcare. From non-invasive therapies to advanced surgeries, there is a solution that fits your specific needs. Recovery is a personal journey, and the right treatment plan depends on your injury and goals. Consult a qualified sports medicine specialist to thoroughly evaluate your condition. They will guide you toward the best option, so you return to your active lifestyle confidently.